Pineapple
Pineapples are most known for their protein digesting enzyme called bromelain! Bromelain breaks down large protein molecules into amino acids that your body can more easily use. The stem of the pineapple contains the highest amount of bromelain. This enzyme has anti-inflammatory properties, accelerates wound healing, and inhibits platelet aggregation (prevents blood clots). (Maurer, 2001) It is commonly supplemented for inflammatory injuries and autoimmune disorders because of its benefits. (Batkin & Taussig, 1988) Pineapples also have large amounts of Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B6, folic acid, and fiber
Vitamin C
Pineapples, kale, and kiwi contain a lot of Vitamin C. 1/2 a cup of pineapple (what is in this recipe) contains 65% of your daily need of Vitamin C! Kiwis are also very high in Vitamin C. One kiwi is at least 85-115% of your daily need, especially when you consume the skin too. The skin of a kiwi contains more fiber and Vitamin C than the actual fruit itself!! One cup of raw kale contains roughly 134% of your daily value in Vitamin C. You get the picture…this smoothie is chalk full of micronutrients and their benefits.
Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin that you need to ingest on a daily basis, because your body does not store it. It aides in growth and repair of all your tissues (skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bones, teeth, etc.) within your body. It also helps your body make collagen! The benefits of collagen are amazing!! Vitamin C is needed to heal wounds, manage blood sugar, improve eye health/vision, and is need to have a proper functioning immune system. (Strohle & Hahn, 2009)
Fiber
Consuming foods that are rich in natural fiber is far better than supplementing your diet with fiber enriched processed foods or a fiber supplement. Natural dietary fiber is found in the cell walls of fruits, vegetables, and grains. Fiber helps keep and balance the pH levels in your intestines. It aides in lowering the risk for developing coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and certain gastrointestinal diseases. (Anderson, et. al., 2009) Eating enough fiber, women an upwards of 25 grams and men 10-15 grams more than that, also lowers blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Fiber has a positive effect on improving and optimizing blood sugars in non-diabetic and diabetic people. Oh, and if all those health benefits were not convincing enough…fiber enhances weight loss!
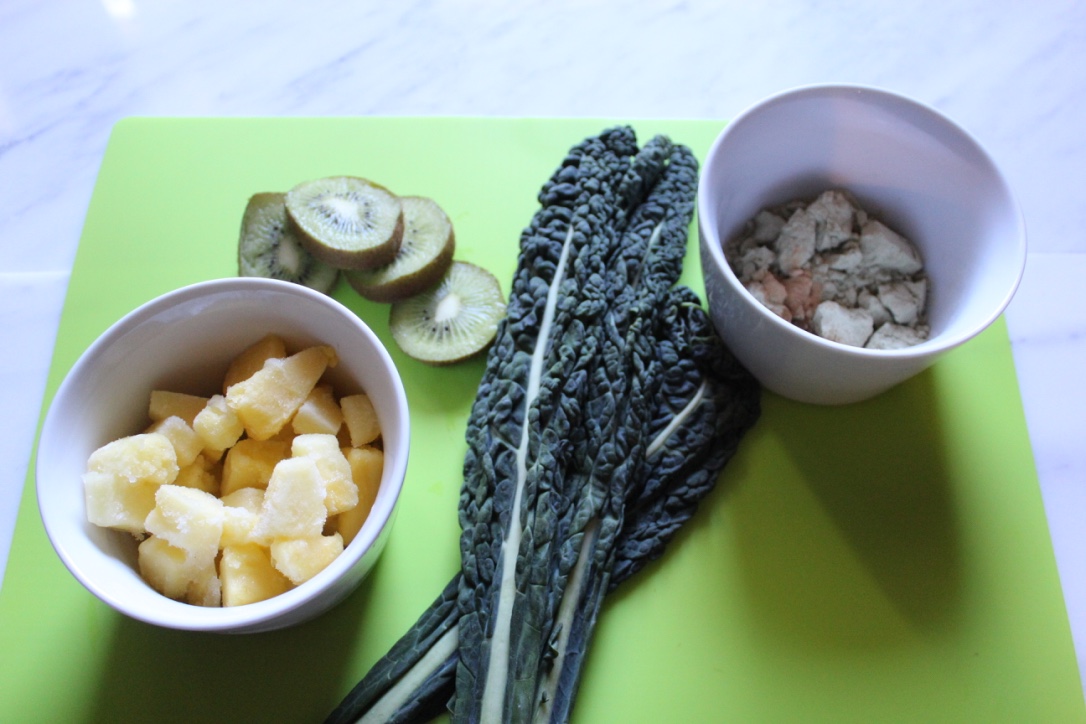
Ingredients
- 1 Handful or 1/2 cup Fresh or Frozen Pineapple
- 3 Organic Kale Leaves
- 1 Organic Kiwi
- 1 Scoop Vanilla Protein Powder
- 1/4 teaspoon Organic Ashwagandha Root Extract
- 1/8 teaspoon Organic Maca Powder
- Spring Water to fill
Instructions
- Wash and clean all veggies and fruit
- Chop kale leaves
- If you are using a fresh pineapple, remove rough skin and dice pineapple
- Leave skin on the kiwi, cut the ends off
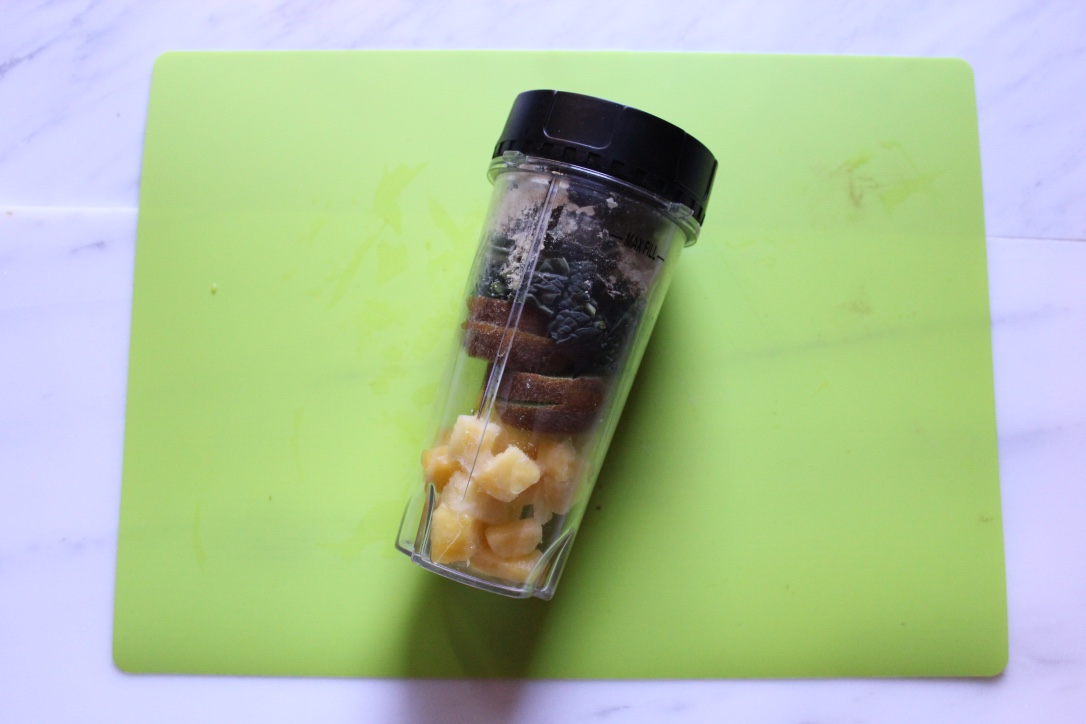
- Combine all fruit, protein powder, ashwagandha, and maca powder in the Ninja Blender
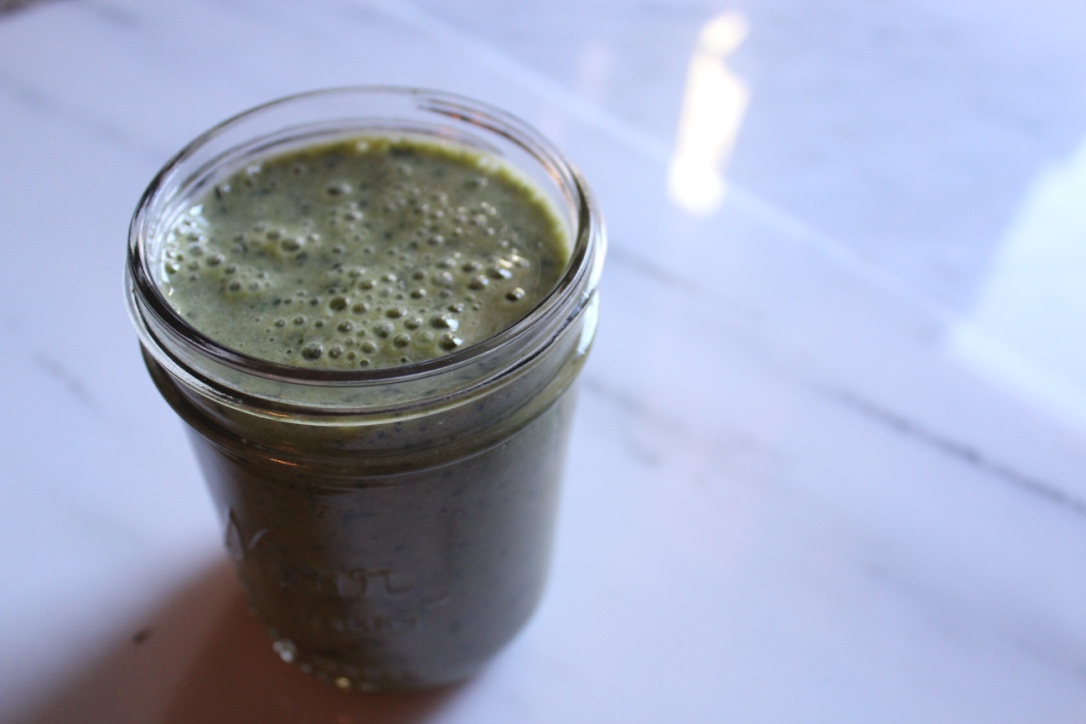
- Add water as desired and blend until smooth!
References
Anderson, J. W., Baird, P., Davis, R. H., Jr., Ferreri, S., Knudtson, M., Koraym, A., . . . Williams, C. L. (2009, April). Health benefits of dietary fiber. Retrieved March 12, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19335713
Batkin, S., & Taussig, S. J. (1988, Feb. & march). Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. Retrieved March 10, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3287010
Kale, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories. (n.d.). Retrieved March 12, 2017, from http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/vegetables-and-vegetable-products/2461/2
http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fruits-and-fruit-juices/1934/2
Maurer, H. R. (2001, August). Bromelain: biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Retrieved March 10, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11577981
Strohle, A., & Hahn, A. (2009, February). [Vitamin C and immune function]. Retrieved March 12, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19263912
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid). (n.d.). Retrieved March 10, 2017, from http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/supplement/vitamin-c-ascorbic-acid